A Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Locus Coeruleus
As we age we lose neurons in the brain. A significant loss of neurons within the Locus Coeruleus (LC) is linked to Dementia and Parkinson’s disease, as it produces norepinephrine and sends it to the cerebral cortex as well as a variety of other structures. Because of the diversity in the actions of norepinephrine and the areas within the body it acts upon, the LC is therefore involved in a large number of core functions within the body and brain, including attention, motor control and vigilance.
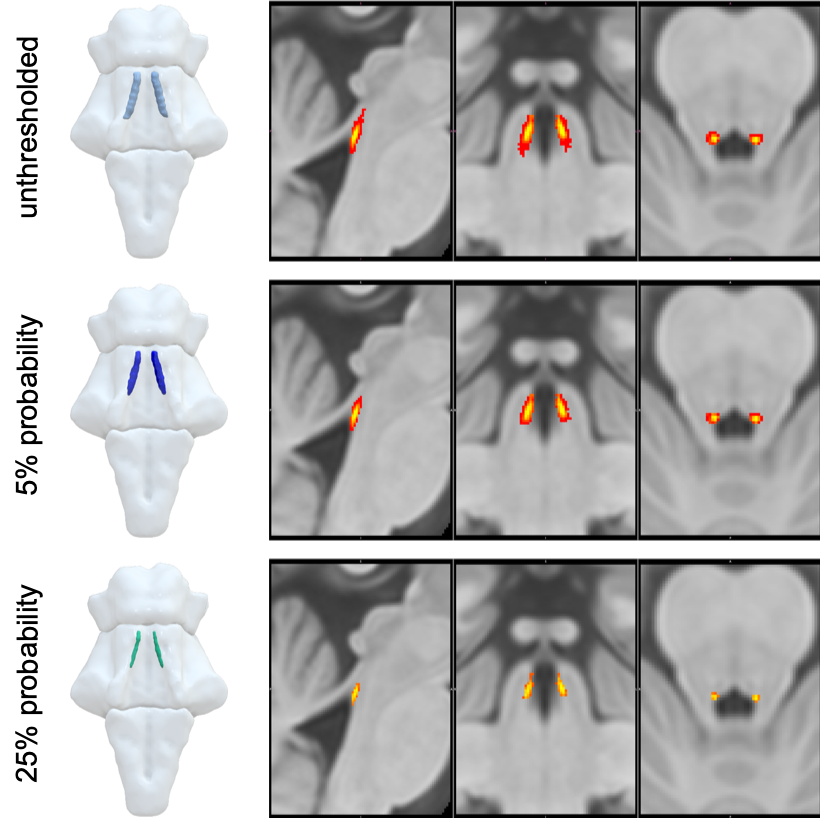
The Brain Atlas
The Brain Atlas is an in vivo 7T Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Locus Coeruleus.
The 7T probabilistic LC atlas is created using magnetisation transfer images from 53 healthy volunteers (52 – 84 years) with ultra-high field 7T MRI. The atlas benefits from improved spatial resolution (0.4 x 0.4 x 0.5 mm) and SNR at 7T, advanced registration and segmentation methods as well as, consistent spatial features comparing to ex vivo findings.
Therefore the Brain Atlas software tool can locate the LC and through this high resolution mapping, enable research to detect and monitor the LC and it’s links to neurodegenerative diseases, supporting research into early signs of disease progression.
Opportunity
The Brain Atlas currently sits within our Research Tools portfolio, is free for Academic use and ready to be licenced out for commercial use.
References
The details for building the atlas and its derived images are described in: Rong Ye, Catarina Rua, Claire O’Callaghan, P Simon Jones, Frank Hubert Hezemans, Sanne S Kaalund, Kamen A Tsvetanov, Christopher Rodgers, Guy Williams, Luca Passamonti, James Rowe; An in vivo Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Locus Coeruleus at Ultra-high Field; bioRxiv 2020.02.03.932087; doi: An in vivo Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Locus Coeruleus at Ultra-high Field (biorxiv.org)